A Beginner’s Guide to a Plant Based Diet (V + WFPB)
Begin a journey towards a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle with our beginner’s guide to a plant-based diet. 🌱 Learn the basics, discover essential tips, and explore delicious recipes to make your transition seamless and enjoyable!

Are you ready to embark on a journey toward better health and sustainability?
This beginner’s guide will help you explore the world of a plant-based diet with an introduction to the types of foods to eat, the benefits, and tips to help you succeed.
Plus, you’ll find helpful information about eating plant-based on a budget and how to ensure you get enough essential vitamins and minerals your body needs to thrive!
🌱 What is a Plant-Based Diet?
A plant-based diet is a way of eating that encompasses foods derived from plants, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, herbs, spices, and plant-based oils. It excludes any animal products such as meat, milk, eggs, or honey.
A plant-based diet can vary in the degree to which it excludes animal products. A strict vegan diet excludes all forms of animal products and by-products. While a vegetarian diet may include small amounts of dairy, eggs, or other animal products.
For further reading: What is the Difference Between Vegan and Vegetarian?
The main focus of a plant-based diet leans on whole, minimally processed foods that provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants. With proper planning, it’s 100% possible to get all the required nutrients your body needs to thrive!
Numerous studies have shown that a plant-forward diet can benefit overall health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Types of Plant-Based Foods to Eat
A plant-based diet includes a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods:
🍓 Fruits
Fruits are essential to a plant-based diet due to their high nutrient and antioxidant content. They are nature’s candy and provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Choose from a wide variety of fruits, such as apples, oranges, bananas, berries, mangoes, and grapes. Aim to consume fruits with varying colors to maximize nutrient intake.
When selecting frozen or canned fruits, opt for those without added sugars or syrups. Dried fruits can also be a healthy option in moderation, but be mindful of their higher sugar content and portion sizes.
🥦 Vegetables
Vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them a crucial component of a vegan whole-food plant-based diet.
Include a variety of leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, root vegetables, and colorful options like bell peppers and tomatoes.
Keep oil to a minimum by opting to steam, roast, or saute with water or vegetable broth instead of oil.
🌾 Whole Grains
Whole grains are a good source of complex carbohydrates, fiber, and essential nutrients like B vitamins, iron, and magnesium. They provide long-lasting energy and promote digestive health.
Choose from various grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole wheat pasta, bulgur, and barley. Incorporate them into meals as a base, side dish, or as part of salads and stir-fries.
🌱 Legumes
Legumes are an excellent source of plant-based protein, fiber, and various micronutrients, including iron and zinc. They are filling, versatile, and affordable!
Options include lentils, chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, pinto beans, and peas. Use them in soups, stews, salads, veggie burgers, and grain bowls.
🥜 Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds provide healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are a delicious addition to a plant-focused diet, adding crunch and texture.
Choose unsalted and raw options such as almonds, walnuts, cashews, chia seeds, flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds. Add them to oatmeal, smoothies, and salads, or eat them as a snack.
Nut and seed butters should be free of sugar and oils.
🥛 Plant-Based Milks
Plant-based milks offer a dairy-free alternative that can be used in cooking, baking, or enjoyed as a beverage.
Select unsweetened, fortified versions to ensure adequate nutrient intake, especially calcium and vitamin D. Common options include almond milk, soy milk, oat milk, and cashew milk.
🌱 Plant-Based Proteins
To meet your protein needs on a vegan diet, incorporate plant-based protein sources like tofu, tempeh, seitan, and edamame. They are nutrient-dense and a terrific source of plant protein.
Tofu and tempeh are made from soybeans, while seitan is made from wheat protein. These protein sources can be used in various dishes, such as stir-fries, salads, and sandwiches.
🌶 Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices are essential for adding flavor and depth to plant-based dishes without relying on added fats, sugars, and sodium. Not only are they delicious, but they also contain health benefits due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties!
Experiment with fresh or dried herbs like basil, cilantro, parsley, and thyme, and spices like turmeric, cumin, paprika, and cinnamon. Use them in marinades, dressings, and sauces, or sprinkle them over your favorite dishes to elevate flavors and enhance your culinary creations.
By incorporating these herbs and spices, you’ll enjoy a diverse and delicious vegan WFPB diet while reaping the health benefits they provide.
Read more about how to stock a Vegan Pantry
🌟 Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
Adopting a plant-based diet offers many benefits:
- Improved overall health: Lower cholesterol and blood pressure, and reduced risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Weight management: The high fiber and nutrient content of WFPB foods can promote satiety and a healthier body weight.
- Enhanced digestion: The fiber in plant-based foods supports healthy digestion and regularity.
- Animal welfare: By avoiding animal products, you contribute to the reduction of animal suffering and exploitation.
- Environmental sustainability: Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact than animal-based diets, promoting a healthier planet.
Read more about the health-related benefits at the National Institute of Health.
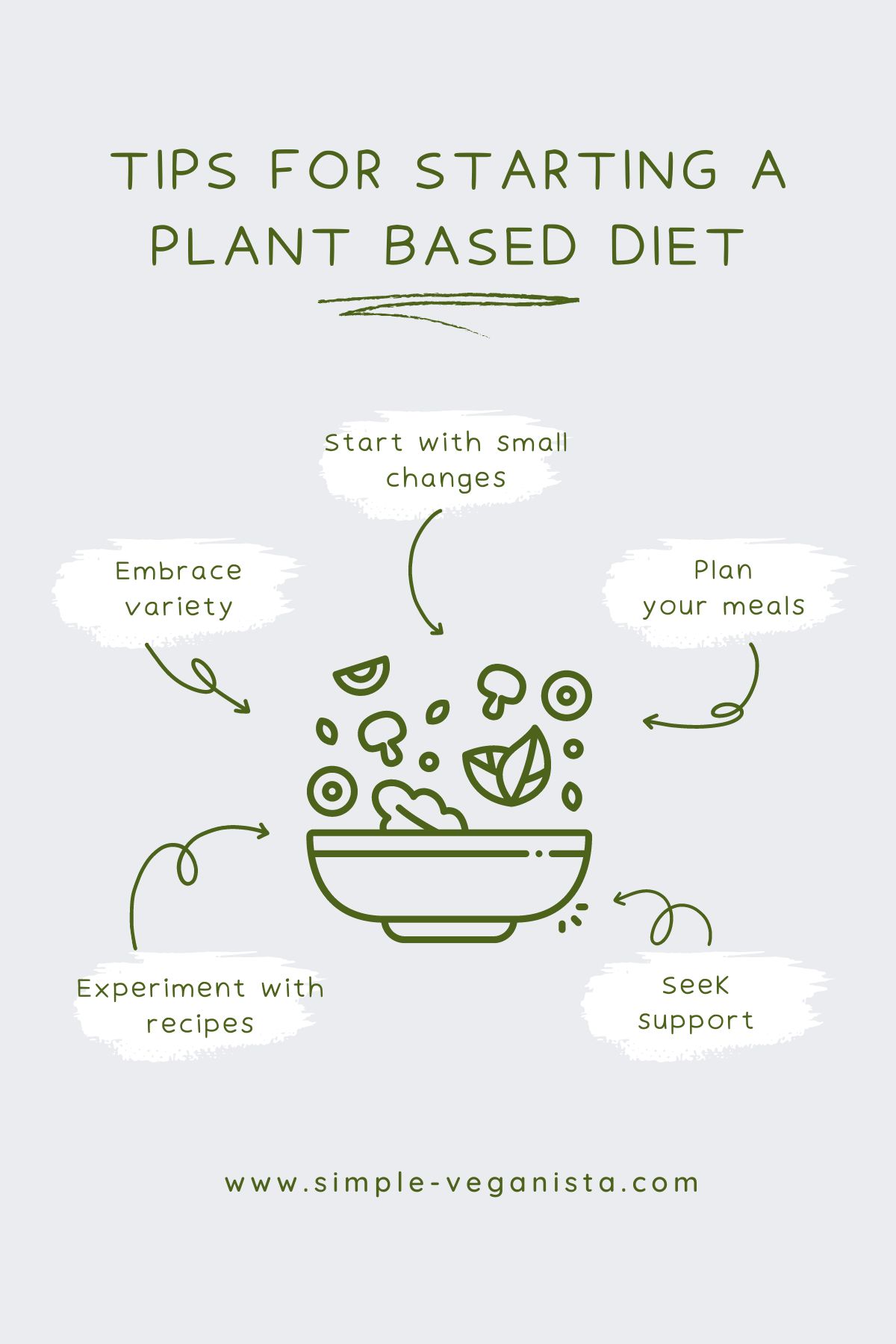
➡️ Plant-Based Tips for Success
As with making any changes in life, the hardest part is beginning and getting through the first month or so. You will need to recondition yourself, but it gets easier as you become more familiar with and adopt a new way of eating. These tips will help!
- Start with small changes: Gradually incorporate plant-forward meals into your diet. Begin by swapping out one meal a day or dedicating specific days to plant-based eating. We find this method very helpful by slowly replacing items, allowing for an easier transition.
- Embrace variety: Eat a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to ensure you get all the necessary nutrients.
- Plan your meals: Meal planning helps you make healthier choices and avoid last-minute temptations.
- Experiment with recipes: Explore new and exciting vegan and WFPB recipes to keep your meals interesting and satisfying.
- Seek support: Connect with others on a similar journey through social media groups, forums, or local meetups for motivation and advice.
❓FAQs
Do I Need to be 100% Plant Based to See Benefits?
While a fully plant based diet offers the most benefits, any move towards incorporating more whole-food plant-based foods into your diet can improve your health and have a positive impact on the planet.
Can I Get Enough Protein on a Plant-Based Diet?
Yes, with a balanced plant-based diet, you can obtain sufficient protein from plant sources like legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, and plant-based proteins such as tofu, tempeh, and seitan. Be sure to check out our guide to high-protein vegetables, which includes plenty of recipes!
What About Supplements?
On a well-planned plant-based diet, the main supplements of concern are vitamin B12, vitamin D, and possibly omega-3 fatty acids.
Nutritional yeast provides vitamin B12 and can be sprinkled on meals. Try to get at least 15 minutes of sunlight a day to help naturally produce vitamin D. Walnuts, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and ground flax seeds are great for omega-3 and can be sprinkled on meals and used in smoothies.
It’s also important to talk to your healthcare provider about appropriate supplementation for your needs.
🌱 Read more about plant-based sources of Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, and Omega-3.
🍽 Take a look at our creative recipes using Nutritional Yeast, Walnuts, Chia Seeds, Hemp Seeds, and Flax Seeds to help get these important ingredients into your WFPB diet.
Can I Still Eat Out?
Absolutely, many restaurants offer vegan and plant-focused options these days. Many are able to accommodate most dietary requests. And if they can’t accommodate you, try ordering a few side dishes to create a meal.
Can I Eat a Plant-Based Diet on a Budget?
Absolutely! It’s possible to follow a plant-based diet on a budget by making smart choices and focusing on affordable, nutrient-dense foods. Here are some tips to help you without breaking the bank:
- Buy in bulk: Purchasing grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds in bulk can save you money. Bulk items tend to be cheaper because you’re not paying for packaging. Just make sure to store them properly to maintain freshness.
- Choose seasonal produce: Seasonal fruits and vegetables are often less expensive and fresher. Buying produce in season can help you save money and enjoy the best flavor and nutritional content.
- Shop at farmers’ markets or local produce stands: Local markets often offer lower prices on fresh produce. Buying directly from farmers can save you money while supporting your local economy.
- Plan your meals: Meal planning helps reduce food waste and ensures you’re using the ingredients you’ve purchased. Make a shopping list based on your meal plan, and stick to it to avoid impulse purchases.
- Cook at home: Preparing your own meals at home is generally more affordable than eating out. Cooking from scratch allows you to control the ingredients and portion sizes while saving money.
- Focus on affordable plant-based staples: Some of the most affordable plant-based foods are also highly nutritious. Focus on items like beans, lentils, whole grains, frozen vegetables, and fruits. These foods are versatile and can be used in various recipes.
- Store brands: Opt for store-brand products instead of name-brand items, as they are often more affordable but still offer similar quality.
- Buy frozen or canned: Frozen and canned fruits and vegetables can be more cost-effective than fresh, especially when out of season. Just make sure to choose those with no added sugars or syrups (for fruits) and low sodium (for vegetables).
By incorporating these tips into your lifestyle, you can enjoy a nutritious, vegan diet even on a tight budget. With a bit of planning and creativity, it’s possible to eat well and save money at the same time!
Plant-Based Diet Recap
What types of food can I eat on a whole food plant-based (WFPB) diet?
Fruits: Fresh or frozen, avoid added sugars and syrups.
Vegetables: Fresh, frozen, or cooked.
Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole wheat, barley, etc.
Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, etc.
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, etc., preferably unsalted and raw.
Plant-based milk: Almond, soy, oat, etc., unsweetened and fortified versions preferred.
Plant-based proteins: Tofu, tempeh, seitan, edamame, and legumes.
Herbs and spices: Fresh or dried, for natural flavor enhancement.
What are tips for beginning and maintaining a plant-based diet?
Start with small changes.
Embrace a variety of vegetables, fruits, grains, and legumes.
Plan your meals.
Experiment with recipes.
Connect with others on the same journey.
How do you get enough protein and vitamins on a plant-based diet?
A well-planned plant-based diet can provide all the essential nutrients your body needs. However, it’s essential to be aware of the nutrients that might require extra attention:
Protein: Found in legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and tofu.
Vitamin B12: Look for fortified plant milk, breakfast cereals, and nutritional yeast.
Omega-3 fatty acids: Include ground flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts in your diet.
Food For Thought
A plant-forward diet can lead to improved health, environmental sustainability, and animal welfare. As you begin this journey, remember to take small steps, embrace variety, and seek support from others on a similar path.
We suggest checking out our Vegan Pantry for more on what to keep in your plant-based pantry. Our Recipe Index and Recipe Roundups will also get you started with easy recipes and meal planning. Happy eating!
